An Enhanced RBMT: When RBMT Outperforms Modern Data-Driven Translators
Overview
Current mainstream translation systems—such as Google Translate, Yahoo Babel Fish, and Bing—perform reliably for high-resource languages but often fail to accurately translate low-resource languages like Bengali, Romanian, and Arabic. Because these systems depend heavily on large parallel corpora for NMT and SMT, many widely spoken languages remain underexplored across both machine translation and broader NLP tasks.
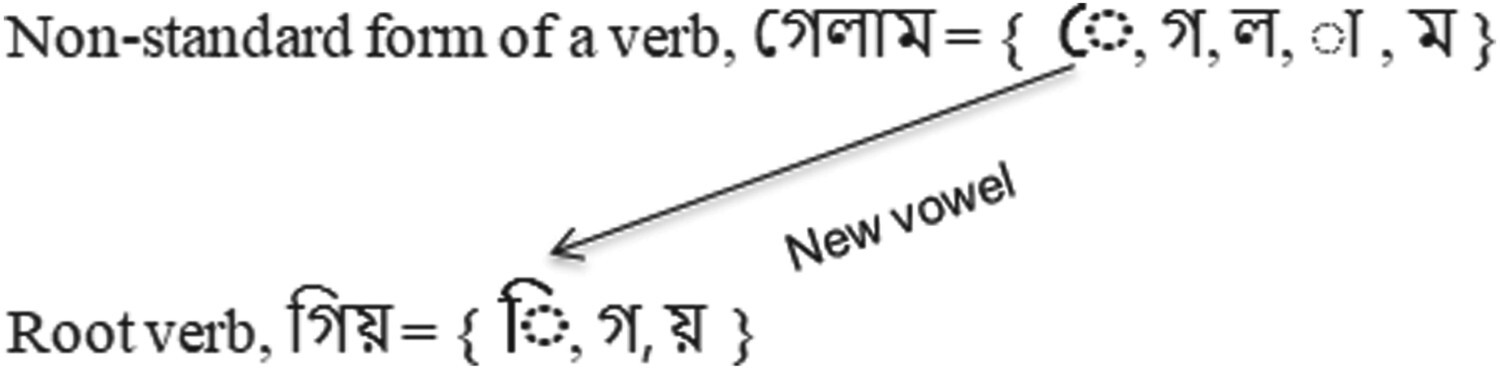
This study addresses this gap by improving Bengali-to-English translation through a refined rule-based MT system. We enhance translation quality by incorporating more accurate handling of Bengali proper nouns as subjects, as well as by strengthening verb processing through root-word identification to better manage the language’s morphological complexity. These linguistic techniques collectively form a more effective framework for low-resource translation. Comparative evaluation against popular data-driven systems using a custom Bengali–English dataset shows that our enhanced rule-based approach delivers superior translation accuracy.
Contribution
My key contribution to this work was designing a novel heuristic for verb root detection that improved both accuracy and space efficiency. This heuristic significantly enhanced the system’s ability to process Bengali verb forms, leading to more precise and reliable translations.